Developer Guide - Diet Manager
Content
- Design
- Implementation
- Product Scope
- User Stories
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Glossary
- Instructions for Manual Testing
Design
Architecture
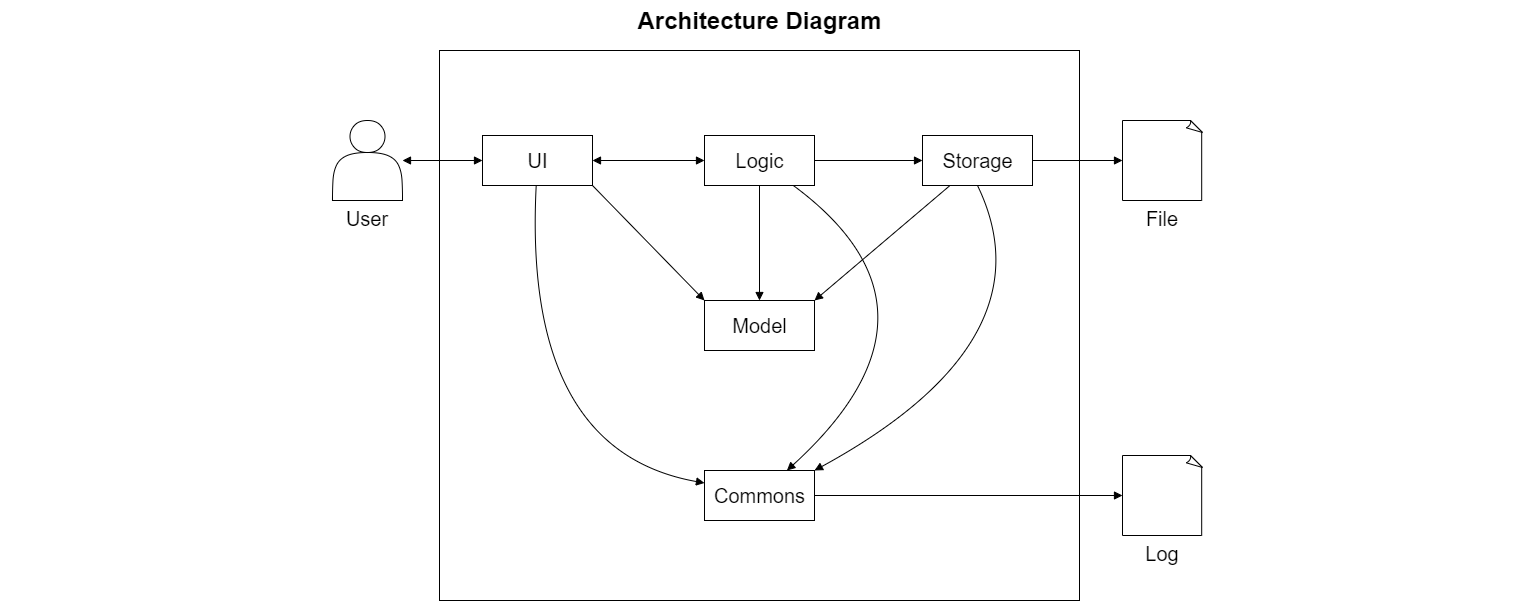
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the Diet Manager Application.
The components involved are given below:
-
UI: The Component responsible for reading user input and displaying command results. -
Storage: The Component responsible for reading, writing and saving of external data files. -
Logic: The Component responsible for managing the logic flow of the application and executing commands. -
Model: The Component responsible for storing information required by the application in-memory. -
Commons: A collection of classes used by multiple other components.
UI component
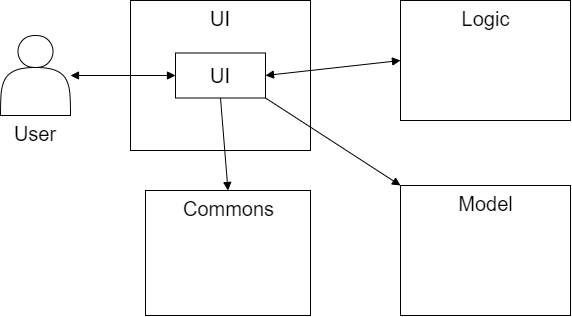
The UI component is responsible for:
- Receiving all command line inputs from the user
- Displaying all system outputs to the user
The UI consists of the following classes:
UI- Reads user input and displays system output
The UI component
- Reads user input and passes it to
Logicfor parsing and execution of the command. - Receives command results from
Logicand listens for changes inModelto display updated information to the user. - Draws on
Commonsto obtain the relevant messages to be displayed to the user.
Storage component
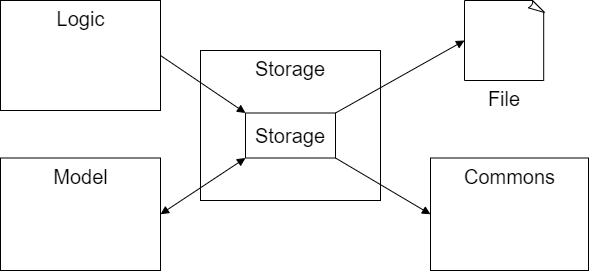
The Storage component is responsible for:
- Reading and loading data files to update the information in local memory during program start up.
- Writing and saving all data into the relevant data files.
The Storage consists of the following classes:
Storage- Stores all user profile information in respective data files
The Storage component
- Reads data files (if present) using
Logicand updatesModelwith the relevant information during start up. - Receives instructions from
logicto save and write in-memory information fromModelinto the relevant data files.
Logic component
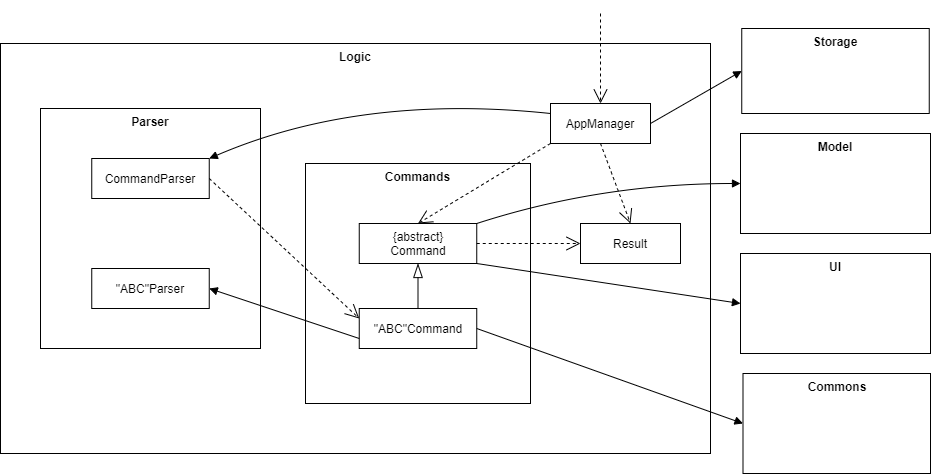
The Logic component is responsible for:
- Establishing the logic flow.
- Deciding how functional components interact with each other.
The Logic consists of the following classes:
AppManager- Arranges the main workflow of the program.Result- Stores the command result in-memory.CommandParser- Parses the user input and generates a specific command."ABC"Parser- A collection of parser classes which parses a specific input to generate a specific value.AgeParser- Parses the user input and generates the user’s age as an integer value between 0 to 150 years old.CaloriesParser- Parses the user input and generates the calories value as a non-negative double.CommandParser- Parses the user input and generates the equivalent Command Object to be processed.DescriptionParser- Parses the user input and generates the String description required by Command.FoodNameParser- Parses the user input and generates the name of the food in lower case for Food Object to process.GenderParser- Parses the user input and generates the profile’s gender as “male” or “female” regardless of upper or lower case input.HeightParser- Parses the user input and generates the profile’s height as a double value between 0 and 300 centimeters.NameParser- Parses the user input and generates the profile’s name as a String.StorageParser- Parses the stored inputs from various data file to generate the user profile, Recipe, Food Record, Time, Weight List and Food Nutrition Record.WeightParser- Parses the user input and generates the profile’s weight as a double between 0 and 500 kilograms.
Command- An abstract class which other command classes inherits from."ABC"Command- A collection of command classes inherited fromCommandwhich perform specific functions.AddFoodCommandAdds food item with food name and nutrition value into theFoodNutritionRecordwhich provide a data bank of food items.BuildNewRecipeCommand- Provides the user with a food recommendation for the week based on the maximum number of food they want per meal, capped at 3, and the activity level.CalculateCaloriesCommand- Calculates the calories intake of the profile in a given specified day or time period of a week.CheckBmiCommand- Provides the BMI table for user to view the category (UNDERWEIGHT, HEALTHY, OVERWEIGHT, OBESE, EXTREMELY OBESE) that he/she is in.CheckRecordCommand- Checks the meal that the profile had consumed on a given day and time period.CheckRequiredCaloriesCommand- Checks the calories intake against the required calories for a day given the activity level.CheckWeightRecordCommand- Checks the weight progress of the profile, to view the weight changes thus far and the weight changes required to meet the weight goal.ClearFoodRecordCommand- Clears all the stored food record of the profile.DeleteFoodCommand- Deletes food item with food name and nutrition value from theFoodNutritionRecordwhich provide a data bank of food items.DeleteWeightCommand- Deletes an incorrect weight record by the record index. Note that the profile must retain at least one weight record as initial weight..ExitCommand- Terminates the program and save all records into external data file.HelpCommand- Provides user with help table that shows list of command that can be executed and how to use them.ListFoodDatabaseCommand- Provides user with a list of all the food items stored in the data bank.ProfileCommand- Provides the current stored profile of the user.RecordMealCommand- Records the meal consumed in a day, Sunday to Saturday, and for a given time period, Morning or Afternoon or Night.SetAgeCommand- Sets the age of the profile.SetGenderCommand- Sets the gender of the profile.SetHeightCommand- Sets the height of the profile.SetNameCommand- Sets the name of the profile.SetProfileCommand- Sets a new profile for the user, with the name, age, gender, height, weight, weight goal.SetWeightCommand- Adds a new weight of the profile for user to monitor weight changes.SetWeightGoalCommand- Sets the ideal weight of the profile.ShowRecipeCommand- Provides the user with the stored food recommendation for the week.
The Logic component
- Receives the user input and parses it to generate a specific command.
- Executes the command to generate a specific result.
- Passes results to
UIto display system output to the user. - Updates
Storageto save any changes made to in-memory information to the respective data files.
Model component
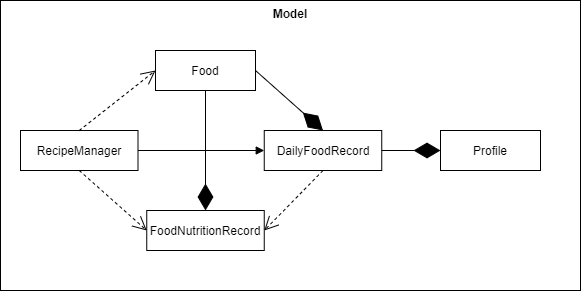
The Model component is responsible for:
- Storing all relevant information in-memory for the application to access.
The Model consists of the following classes:
Profile- Stores the personal information of a person including the name, age, gender, height, weight, weight goal, list of food consumed and list of weight changesDailyFoodRecord- Keeps a record of the food consumed in a day, comprising morning, afternoon and nightFood- A food object which contains the relevant food informationFoodNutritionRecord- Provides a data bank of food items with the food name and calories valueRecipeManager- Generates and stores recipes depending on user information
The Model component
- Receives instructions from
Logicto update in-memory information. - Is not dependent on any of the other components.
- Contains all the classes that are responsible for database and records of food and user
Commons component
The Commons component is responsible for:
- Consisting of multiple useful classes which are utilised by other components in the application.
The Commons consists of the following classes:
LogsCentre- Tracks system through log records and saves them into a log fileMessageBank- Consists of multiple standard system output messages for UI to printWeekday- Enumeration class for classifying all 7 possible days in a week"ABC"Exception- A collection of exceptions to aid in running of the applicationInvalidAgeException- Exception that is thrown when when user inputs age format that is not integer or when the user provides an age that is not within 0 and 150 years old.InvalidCaloriesException- Exception that is thrown when the user inputs a calories value that is not double or when the user provides a calories value that is negative.InvalidCommandException- Exception that is thrown when the user key in a Command that does not exists.InvalidFoodNameException- Exception that is thrown when the user did not input any String food name.InvalidFormatException- Exception that is thrown when the user input a command that is not of the right number of argument.InvalidGenderException- Exception that is thrown when user input gender format that is not “male” or “female” regardless of upper or lower case input.InvalidHeightException- Exception that is thrown when user inputs height format that is not double or when the user provides a height that is not within 0 and 300 centimetres.InvalidNameException- Exception that is thrown when the user did not input any String name.InvalidWeightException- Exception that is thrown when user inputs weight format that is not double or when the user provides a weight that is not within 0 and 500 kilograms.NegativeNumberException- Exception that is thrown when the user input negative number for the number of food item in build receipt command.
Implementation
Launch Application
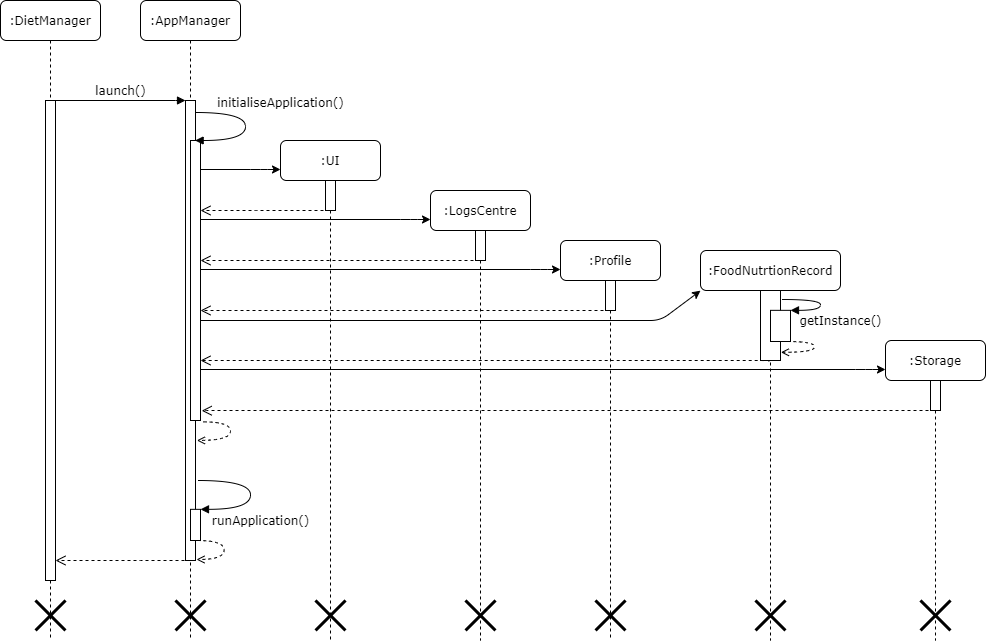
Implementation
Upon startup of Diet Manager:
AppManager.launch()is called.AppManagerthen constructs the relevant object required for the application to function. These objects include, in the order of construction:UI- User Interface functionsLogsCentre- Logging and system tracking functionsProfile- Holds user profile data in-memoryFoodNutritionRecord- Holds food nutrition data in-memoryStorage- Prepares data files for reading, writing and saving of information
- Once the objects have been created,
Storagethen loads any current data from data files (if any) into local memory for the application to access. If no data files are found,Storagecreates new data files for future storage. - All relevant components have now been initialised and the application is ready to be run.
Design and Enhancements
The modular system of initialising the application serves several purposes:
- Reducing coupling and dependence between essential components upon startup
- Aid in debugging by isolating the components
- Future enhancements which might include the construction of additional components
This implementation can be further enhanced by further abstracting initialisation of different components, which would be useful in the future when more components are added to enhance this application.
Logic Management
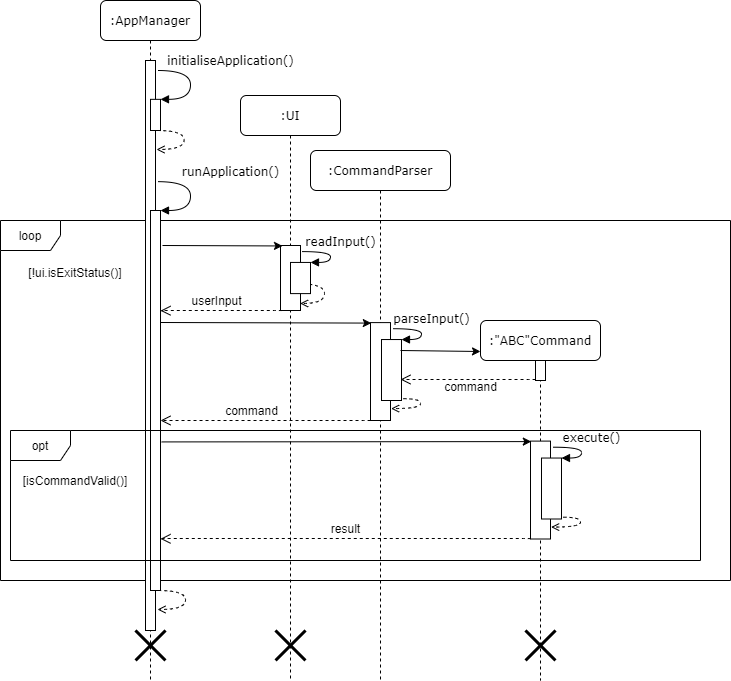
Implementation
The logic flow of DietManager was intentionally made to be modular in design, and allow AppManager to be the sole handler of all logic-based executions.
Upon running the application:
- A check is done for the
ui.exitStatus()of the application, and exits the loop if the user entered the exit command during the previous iteration. UIcallsreadInput()to read in user input.- The String value of user input then gets passed back to
AppManager. - The String value then gets parsed through
CommandParserto generate a specificCommand. - This command will then be passed back to
AppManager. AppManagerchecks if the command is valid usingisCommandValid().- If the command is valid, AppManger executes the command using
execute(). - The command
Resultthen gets returned toAppManager, where it will be displayed to the user. - The loop then continues, from steps 1 to 9.
- If the user exits the application, the application will terminate and all created components will be destroyed.
Design and Enhancements
The modular system of running the application serves several purposes:
- Reducing coupling and dependence between essential components upon startup
- Aid in debugging by isolating the components
- Future enhancements which might include the construction of additional components
The design of AppManager was done to prevent the possibility of errors occurring in multiple components due to potential bugs, and narrows down the scope of potentially flawed components.
This aids in testing and debugging of the application, as well as leaves space for future enhancements, by allowing other components to interact with the application without having to change multiple different components to achieve this. This allows for greater accessibility and modularity.
This implementation can be further enhanced by abstracting the logic flow of different components into separate classes. Thus each individual class will be responsible for the logic management of a particular component thus would allow for more modularity, testability and expandability.
Record Meal Feature
Implementation
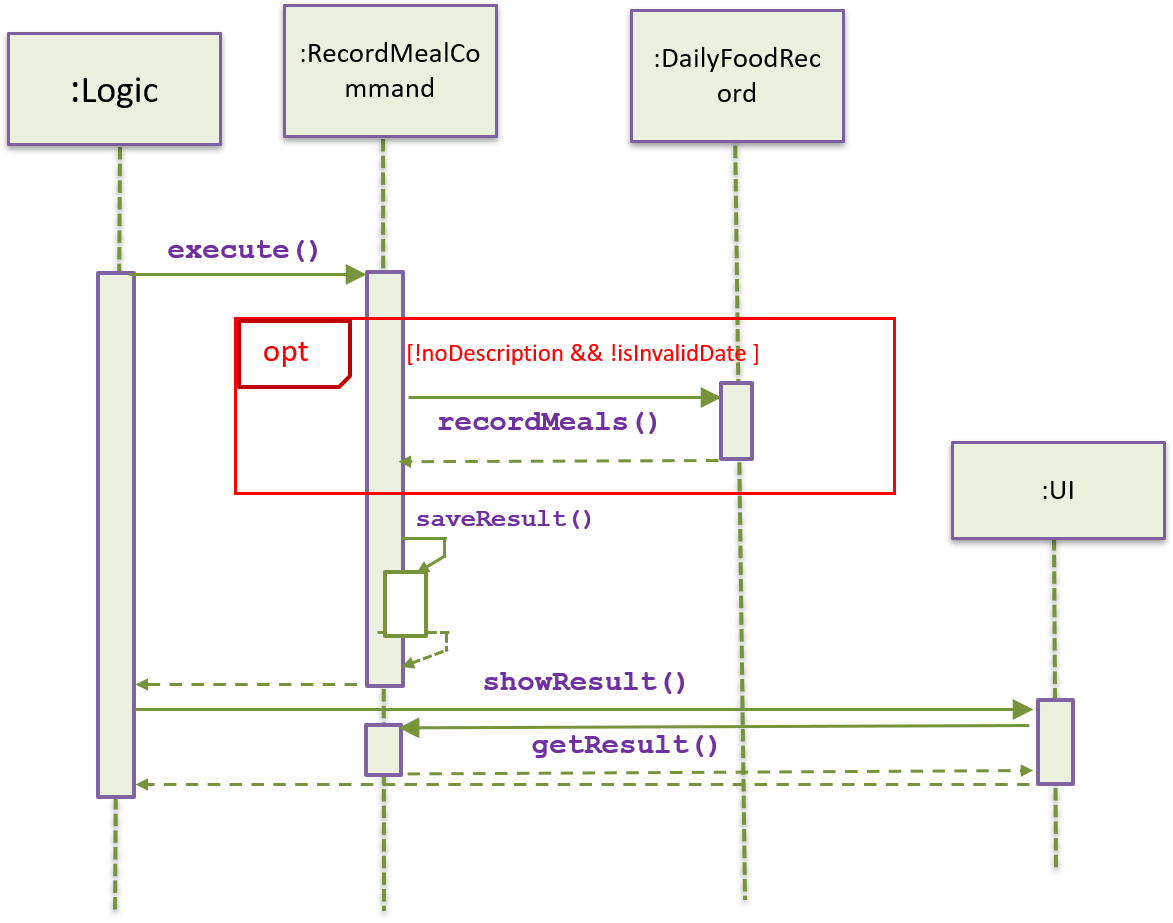
The record feature is facilitated by RecordMealCommand. It extends Command and overrides execute() and saveResults()
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the record mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The ui object gets user input and sends it to the parser. The parser then parses the original input into a standard command
and returns it. The command type is decided by the commandPrompt. The RecordMealCommand has record-meal as its commandPrompt.
During the process a newRecordMealCommand object will be generated and returned to the Logic component.
Step1. Generate command
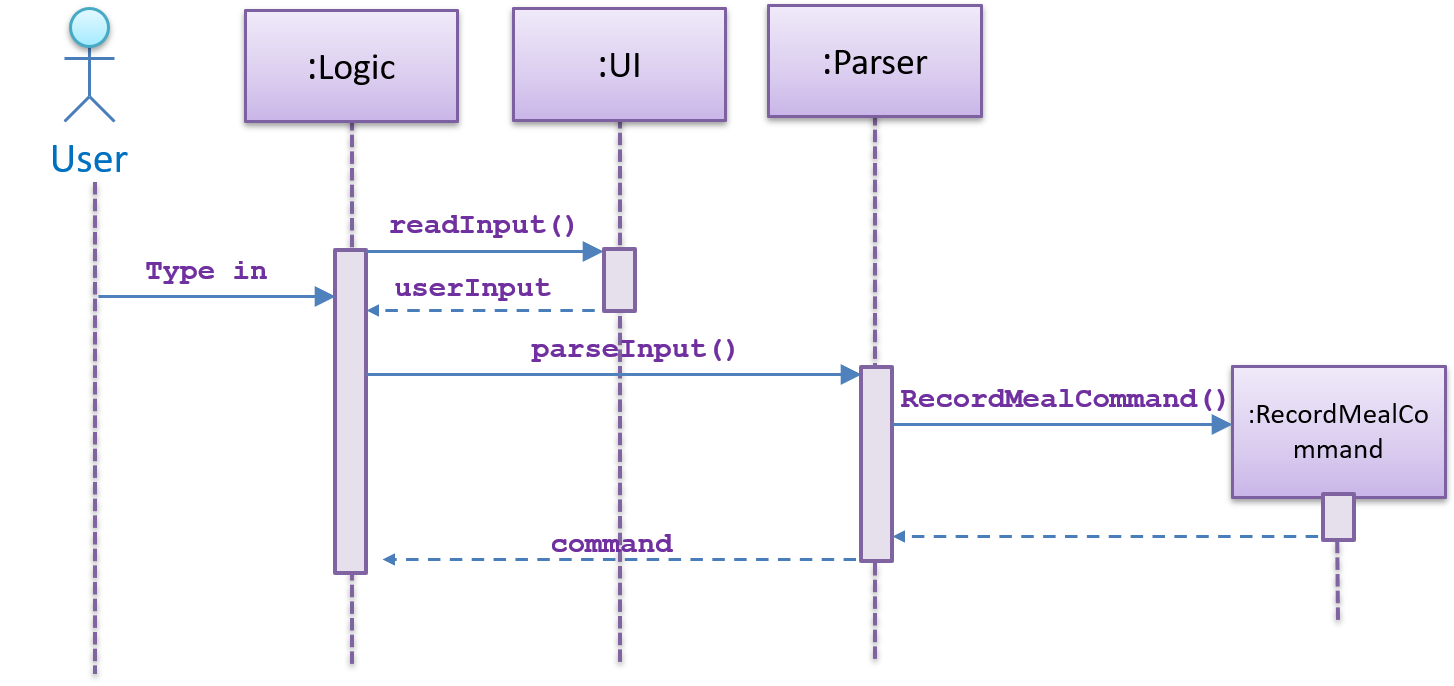
Step 2. The Logic composition calls the execute() method of the RecordMealCommand object.
During the process of execution, the command object will generate a ArrayList<Food> foodList, which maintains all Food items listed in the user input.
If a certain kind of Food can be found in the database of FoodNuritionInfo, then this food item will be fetched from the database.
Else a new Food object will be generated simply with foodName without all the nutrition info.
During execution, the command object will try to get a record object of the class DailyFoodRecord. The date of record is specified by the user.
If no record of that day is found in profile, it will automatically generate a new record of the day. Then with foodList and record, can call
the method record.recordMeals().
Step2. Execute and Save Result
Design Considerations
Aspect: How RecordMealCommand executes and save results
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Directly operate on the
Profileobject, more specifically, theDailyFoodRecordattribute inProfileobject. And save executionresultsin theRecordMealCommandobject.- Pros: Logic is clear and easy to implement.
- Cons:
Commandobject has full access toProfileobject, which is not safe.
- Alternative 2:
RecordMealCommandcan only operate onDailyFoodRecordof theProfile.- Pros: Reduce dependency and potential risks.
- Cons: Different types of
Commandneed different declarations/interface forcommand.execute()method.
Aspect: Data structure to support the command
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Use a list to store daily food record for a profile.
- Pros: Easy to implement and understand
- Cons: The list is maintained by a
Profileobject. Can lead to more duties for aProfileobject.
- Alternative 2: Use a
FoodHistoryManagerto keep record of daily meals.- Pros: More OOP.
- Cons: Makes the execution procedure more complex.
Product Scope
Target user profile
Students that :
- are too busy with schoolwork to carefully monitor their eating habits
- are concerned about their health
- likes to keep track of their meals/weight habit digitally
- want to keep track of their weight
Value proposition
Diet Manager aims to achieve the following:
- Streamline the diet recording and monitoring process
- Allow users to track food calories intake and monitor their eating habits
- Enable users to monitor weight changes over time and work towards their ideal weight goal
- Provide personalised health information and dietary recommendations for the user
- Monitor and track user’s weight changes to achieve weight goal
- Check their BMI as well against the BMI table regardless of user
User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | student | set a profile with personal information | receive personalised information regarding my diet |
| v1.0 | student | record my calories intake | can keep track of my total calorie intake for the week effectively |
| v1.0 | student | record my food intake | see what I ate today |
| v1.0 | student | see my diet history | can track my diet and maintain a balanced and healthy diet lifestyle |
| v1.0 | student | set a weight-goal | received feedback on progress regarding my weight goal |
| v1.1 | student | record my weight changes | can see if i am doing well towards my expectation |
| v1.1 | student | check nutritional values of certain foods | can check how much calories i am consuming |
| v1.1 | student | check if I am keeping to my recommended caloric intake | do not over or under eat and maintain my diet |
| v1.1 | student | add food items to the database | do not have to constantly check food nutritional value for common foods |
| v1.2 | student | save my diet history | have a record of my daily food intake |
| v1.2 | student | save my profile | do not have to constantly set a new profile |
| v1.2 | student | import my diet history | have access to previous records and be able to progress from there |
| v1.2 | student | receive dietary advice based on my excess calorie intake for the day | can maintain my calories for the day |
| v1.2 | student | export my diet history | can view my previous records on other devices and never ever lose my progress |
| v2.0 | student | generate a recommended food plan | know what to eat to meet recommended caloric intake |
| v2.0 | student | save and export my food plan | print it out or bring it with me |
Non-Functional Requirements
Device Environment:
- Must have Java 11 or higher installed in OS
- 32-bit or 64-bit environment
- Command Line Interface or Terminal for Mac
Performance:
- Function offline, without the need for internet access
- Quick to launch and use
- No noticeable lag or delay in performance when running
- Intuitive and seamless for new users.
- Ability to export the data into a txt file to load on another OS
Reliability:
- Data files should be updated constantly and accurately, with no data loss
- Data records should be retrievable and readable
- Text inputs should produce similar results if utilised multiple times.
- Program should run without any forced-close error due to bugs
Glossary
- NAME - Standard form for name is a String value with no spaces
- FOOD-NAME - Standard form for food name is a String value with no spaces
- AGE - Standard form for age is an int value more than 0 and less than 150
- GENDER - Standard form for gender is a String value of “male” or “female”
- HEIGHT - Standard form for height is a double value more than 0 and less than 300, standard unit kilograms
- WEIGHT - Standard form for weight is a double value more than 0 and less than 500, standard unit centimetres
- WEIGHT-GOAL - Standard form for weight goal is a double value more than 0 and less than 500, standard unit centimetres
- CALORIES - Standard form for calories is a double value more than 0, standard unit kilocalories
- INDEX - Standard form for index is an int value, depending on the size of the corresponding list
- DATE - Standard form for date is restricted to the range of MONDAY to SUNDAY
- TIME-PERIOD - Standard form for time period is MORNING, AFTERNOON, NIGHT
- ACTIVITY-LEVEL - Standard form for activity level is LOW, MODERATE, HIGH
- profile.txt - Data file containing user profile information
- daily-food-record.txt - Data file containing user daily food record information
- food-nutrition-record.txt - Data file containing food nutrition record database
- recipe.txt - Data file containing user generated recipe list
Instructions for Manual Testing
For manual testing, developers can follow the instructions listed out in the UserGuide
- Detailed input and output examples are displayed for cross checking.
Alternatively, they can also follow the following steps to test out the respective commands, upon downloading the jar file, while adhering to the specified restrictions in Glossary:
set-profile NAME AGE GENDER HEIGHT WEIGHT WEIGHTGOAL- Creates a new profile
profile- View user profile details
set-name NAME- Update name in profile.
set-age AGE- Update age in profile.
set-age GENDER- Update gender in profile.
set-height HEIGHT- Update height in profile.
set-weight-goal WEIGHT-GOAL- Update weight-goal in profile.
set-weight WEIGHT- Update weight in profile.
delete-weight INDEX- Delete a specific weight record.
check-weight-progress- Check user weight record progression.
check-bmi- Check user BMI and BMI classification.
record-meal DATE TIMEPERIOD /FOOD1 {-- 10.0} /FOOD2 {-- 6.00} /...- Record a meal
check-meal DATE TIMEPERIOD- Check a meal
clear-records- Clear all food records
check-required-cal DATE ACTIVITYLEVEL- Check calories required based on user’s activity level
calculate {DATE1}->{DATE2}- Calculates calories intake on a day or during a time period
list-food- List all foods recorded in the database
addf FOODNAME --CALORIES- Add a new food into database
delf FOODNAME- Delete a food from the database
new-recipe MAXIMUM_FODD_TYPES ACTIVITY_LEVEL- Create a recommended recipe for user
show-recipe- Show the recipe recommended for user
help- Show the help function table with supported commands.
exit- Terminates and exits the application.
Click here to go back to the main page.